Dog Gum Disease: Symptoms, Causes, Effects, and Treatments
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common health condition that affects dogs.
It is caused by the accumulation of bacteria on the teeth, leading to inflammation and infection of the tissues that surround the dog’s teeth12.
If left untreated, it can cause significant harm to a dog’s mouth, including eroded gums, bad breath, missing teeth, bone loss, and chronic pain2.
Symptoms
In the early stages of gum disease, there are often no obvious signs2.
By the time symptoms are noticed, the pet may be in advanced stages2.
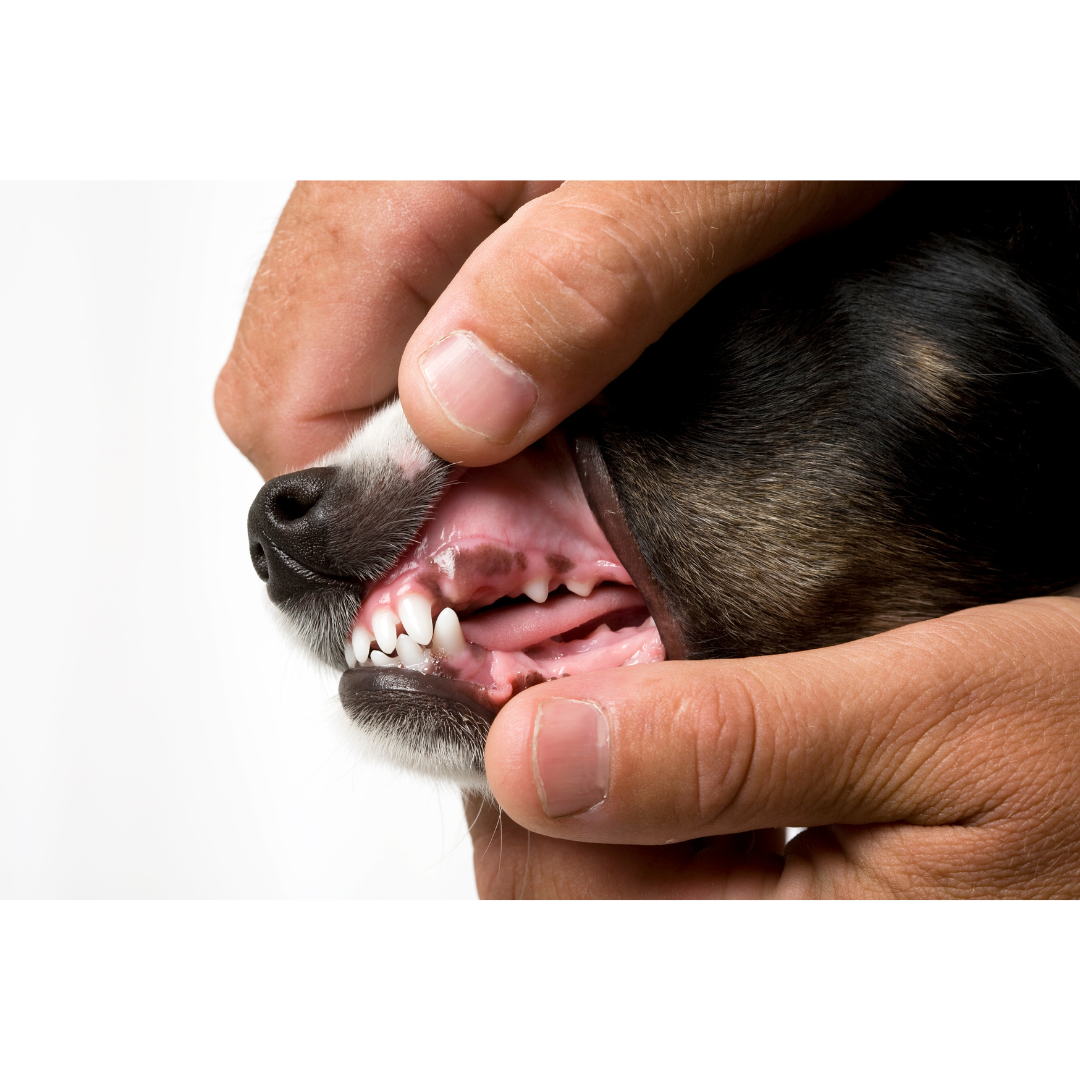
Symptoms of advanced periodontal disease include:
- Bleeding or red gums
- Pawing at the mouth
- Loss of appetite
- Difficulty eating
- Drooling
- Irritability or anti-social behavior
- Loose or missing teeth
- Blood in water bowl or on chew toys
- Bad breath23
Causes
Gum disease begins with bacteria, food, and saliva combining to form plaque.
The plaque coats the teeth and, within 2-3 days, combines with minerals and hardens into tartar2.
Our body’s immune system attempts to fight the bacteria in plaque and in turn causes the gums to become red and inflamed2.
Some factors that contribute to the development of gum disease include:
- Age
- General health
- Diet
- Chewing behaviors
- Genetics
- Tooth alignment
- Grooming habits
- Dental hygiene2
Effects
Periodontal disease can have serious consequences for your dog’s overall health and quality of life1.
It can cause chronic pain, gum erosion, and loss of bone and teeth4.
The structures supporting the teeth can also be weakened or lost4.
In severe cases, it can lead to the tooth completely losing its attachment from its socket, leading to the tooth becoming loose or falling out1.
Treatments
The treatment for gum disease depends on the specific problem and the stage of the disease.
In the early stages of gum disease (stage 1), it can be treated with regular tooth brushing and good oral health care5.
Mild to moderate periodontitis (stages 2 and 3) requires scaling above and below the gum line to remove plaque and tartar build-up5.
In severe cases (stage 4), tooth extractions may be necessary to remove any damaged teeth6.
It is also important to follow your veterinarian’s instructions for at-home care6.
Conclusion
Gum disease is a common but serious health issue in dogs.
Regular dental hygiene and check-ups with the vet can help prevent this disease and ensure your dog’s oral health.
If you suspect your pet may have symptoms of gum disease, it is important to bring your pet to the veterinarian for an oral examination2.
Love you canine companion more and show affection creatively.
Visit our shop for our awesome pet inspired graphic t-shirt collection wear it proudly and let the world know just how much your furry friend means to you.
FREE SHIPPING and use
PPS10 discount code for 10% off your first purchase.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only. It is not meant to substitute for medical advice or diagnosis provided by your veterinarian. If your dog shows symptoms, please consult your veterinarian immediately.



Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.